This function compares future climate projections from multiple General Circulation Models (GCMs) based on their similarity in terms of variables. It calculates distance metrics and plots the results on a heatmap.
Usage
dist_gcms(
s,
var_names = c("bio_1", "bio_12"),
study_area = NULL,
scale = TRUE,
method = "euclidean"
)Arguments
- s
A list of stacks of General Circulation Models (GCMs).
- var_names
Character. A vector of names of the variables to compare, or 'all' to include all variables.
- study_area
An Extent object, or any object from which an Extent object can be extracted. Defines the study area for cropping and masking the rasters.
- scale
Logical. Whether to apply centering and scaling to the data. Default is
TRUE.- method
Character. The correlation method to use. Default is "euclidean". Possible values are: "euclidean", "maximum", "manhattan", "canberra", "binary", "minkowski", "pearson", "spearman", or "kendall".
Value
A list containing two items: distances (the calculated distances between GCMs) and heatmap (a plot displaying the heatmap).
Examples
var_names <- c("bio_1", "bio_12")
s <- import_gcms(system.file("extdata", package = "chooseGCM"), var_names = var_names)[1:5]
study_area <- terra::ext(c(-80, -70, -50, -40)) |>
terra::vect(crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
dist_gcms(s, var_names, study_area, method = "euclidean")
#> CRS from s and study_area are not identical. Reprojecting study area.
#> $distances
#> ae cc ch cr
#> cc 0.2454582
#> ch 0.9281454 1.0138236
#> cr 0.8599514 0.9406321 0.1267409
#> ev 0.5924451 0.7399979 0.4275583 0.4008307
#>
#> $heatmap
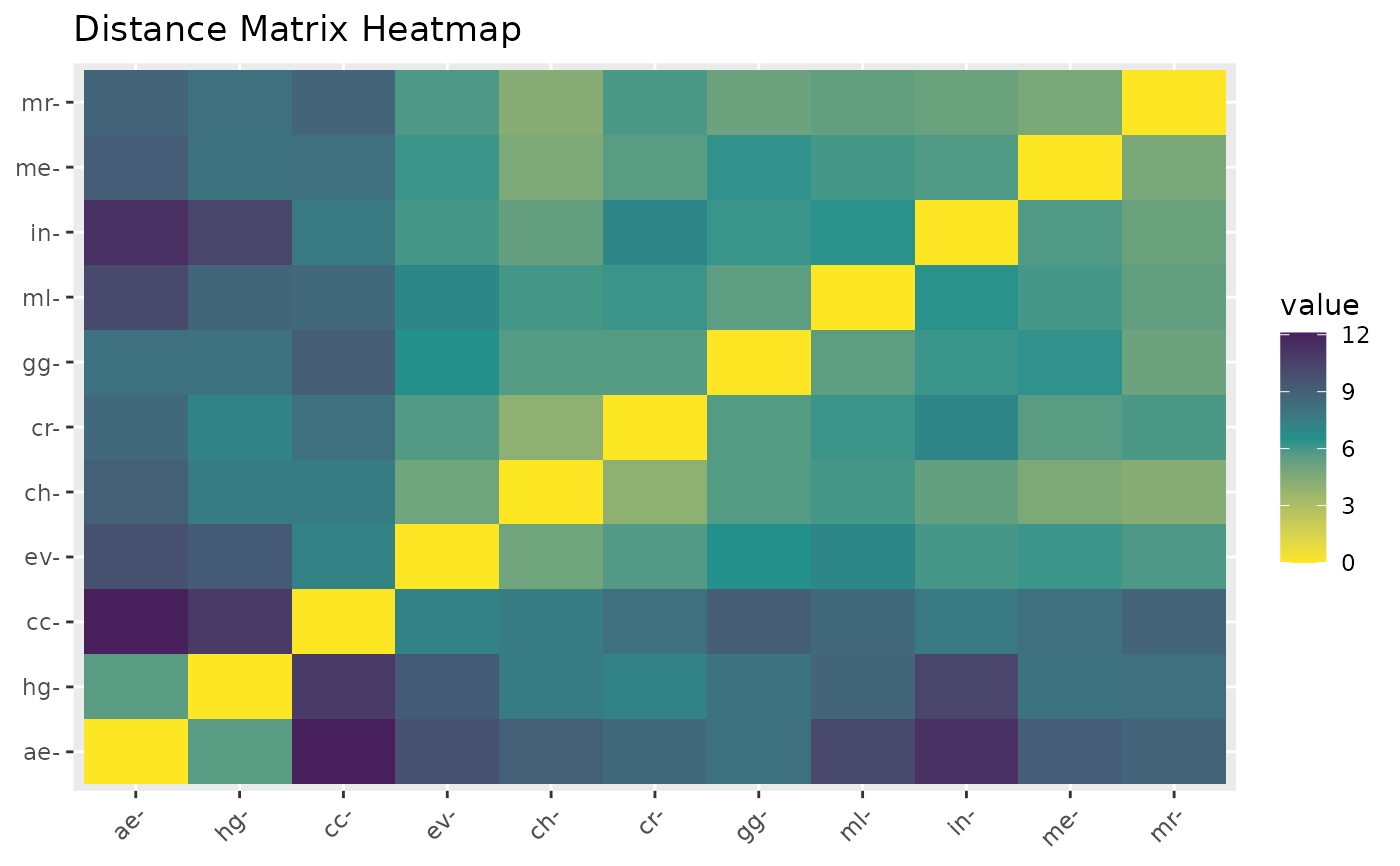 #>
#>
