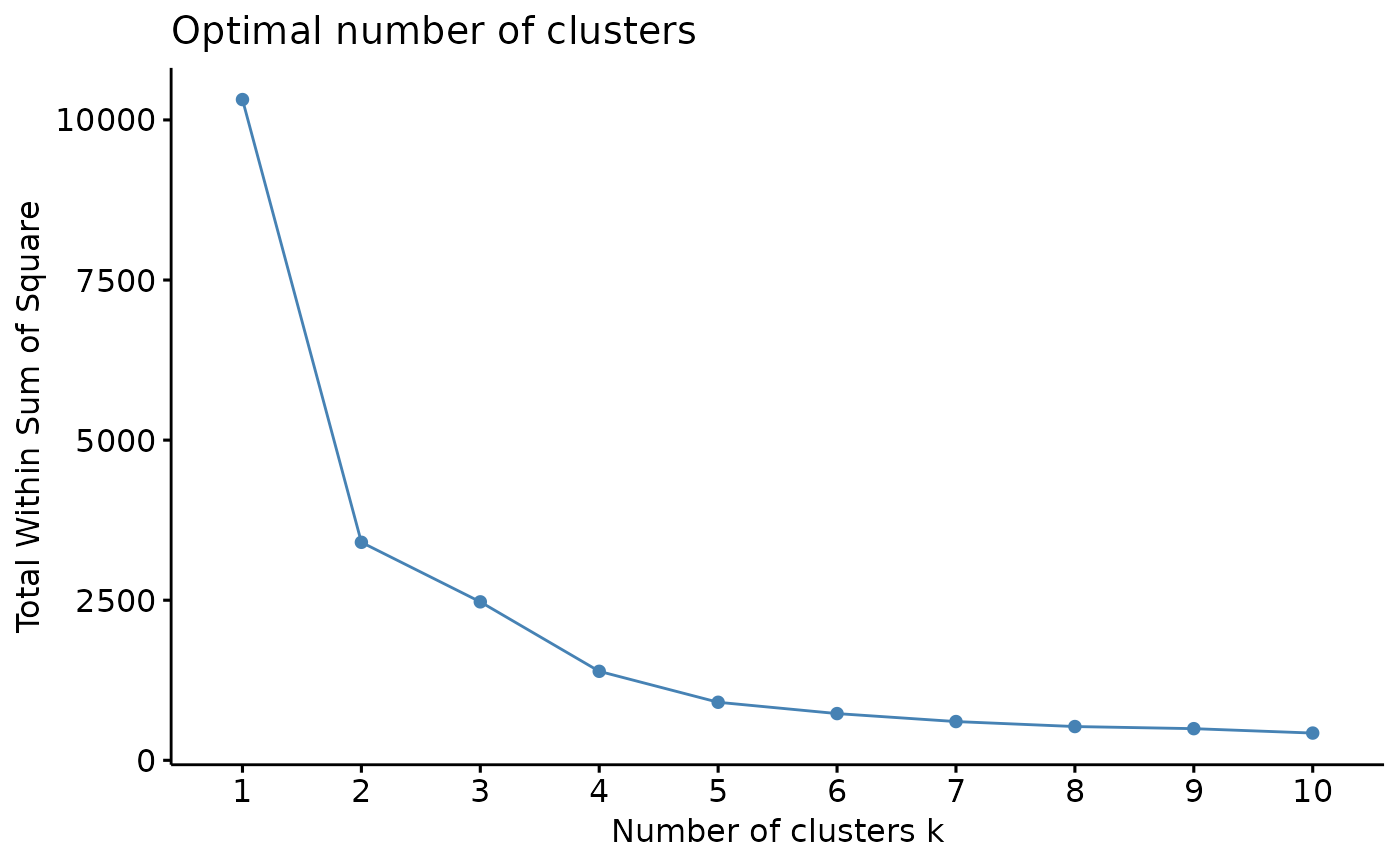
This function performs clustering analysis on a dataset and determines the optimal number of clusters based on a specified method.
Usage
optk_gcms(
s,
var_names = c("bio_1", "bio_12"),
study_area = NULL,
cluster = "kmeans",
method = "wss",
n = NULL,
nstart = 10,
K.max = 10,
B = 100
)Arguments
- s
A list of stacks of General Circulation Models.
- var_names
Character. A vector with the names of the variables to compare OR 'all'.
- study_area
Extent object, or any object from which an Extent object can be extracted. An object that defines the study area for cropping and masking the rasters.
- cluster
A character string specifying the method to build the clusters. Options are 'kmeans' (default) or 'hclust'.
- method
A character string specifying the method to use for determining the optimal number of clusters. Options are 'wss' for within-cluster sum of squares, 'silhouette' for average silhouette width, and 'gap_stat' for the gap statistic method. Default is 'wss'.
- n
An integer specifying the number of randomly selected samples to use in the clustering analysis. If NULL (default), all data is used.
- nstart
Numeric. The number of random sets to be chosen. Default is 10. Argument is passed to `stats::kmeans()`.
- K.max
Numeric. The maximum number of clusters to consider. Default is 10. Argument is passed to `factoextra::fviz_nbclust()`.
- B
Integer. The number of Monte Carlo (“bootstrap”) samples. Default is 100. Argument is passed to `cluster::clusGap()`.
Examples
var_names <- c("bio_1", "bio_12")
s <- import_gcms(system.file("extdata", package = "chooseGCM"), var_names = var_names)[1:5]
study_area <- terra::ext(c(-80, -70, -50, -40)) |>
terra::vect(crs="+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs")
optk_gcms(s, var_names, study_area)
#> CRS from s and study_area are not identical. Reprojecting study area.